Grafka
A Grandjs Package helper for applying event driver architecture on your monolothic application
About
Grafka is a typescript package that helps you write high scalable web application using event driven architecture inside your monolothic application, so instead of calling your services inside the other functions, you can easily inject your services inside Grafka brokers and just fire event from anywhere inside your application and your services will work as a charm!
Features
- Applying Event Driven Architecture on the level of app
- Isolation between your services and controllers
- Connect your services, controllers, repositories event without injecting your dependencies
Use Cases
Imagine you have a nodejs application that has users register, so when the user registers you should send an email or sms verification to verify his account, this action can be done normally by calling the mail service inside your controller and after saving the new user in the database, you call the mail service or sms service directly in your controller to send the verification But Grafka allows you to make your controller does one function which is for example saving the user in database, and then you use Grafka producer to trigger/fire an event and on the other hand you have consumers that listen for this event to work on so easily you can fire event, pass user data through this event and the consumer will call the mail service and send the verification automatically!
- Multiple services works on the same data at the same time
- services that should do an operation but being isolated from other services
Prerequisites
- install nodejs on your machine/javascript browser
- install typescript/javascript
- initialize a new typescript project/javascript project
Dependencies
Grafka doesn't use dependencies to start using it unless you want to use Grafka decorators so you need to install and use typescript
Installing
npm i grafka
Usage
Grafka exposes to you a set of functions and classes that you can use to build your brokers, events and so on
import {Broker, UseBroker, Consumer, UseConsumer, Brokers, useProducer} from "grafka"
Architecture
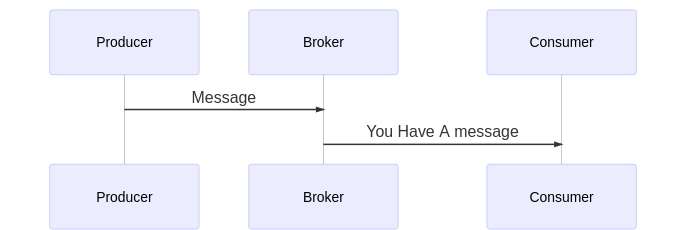
Grafka includes four main instances
- Broker: Grafka exposes a Broker class that you can extend to build your own broker, This broker basically stores your consumers and topics
- Topic: This is the path/name of message that your consumers inside the broker interested in
- Producer: This instance is resbonsible on producing messages and these messages are sent to the broker and listened by the event emitter
- Consumer: Each Topic inside a broker has group of consumers that they are interested in to get updates of that topic once a producer triggers an event
Grafka Event Life Cycle
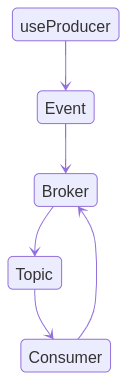
Broker
Grafka Broker is an abstracted class that you can use to build a new broker instance which will host your topics, producers, consumers
Example
import {Broker} from "grafka";
To create a new Grafka Broker instance, you just need to instantiate this class ass the following:
import {Broker} from "grafka";class UserBroker extends Broker{}
Now You have an extended broker which you can use to add topics and consumers to it
Topic
To define a new topic for this broker you can use a decorator called Topic this decorator is a function that takes one argument which is a string refers to the path of the topic you want to create
| property | type | required | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| topic | string | true | the path of the topic you want to create |
Example
import {Broker, Topic} from "grafka";@Topic("/notification")class UserBroker extends Broker{}
This will automatically inject a topic inside your broker, this topic path will be used later from the consumer to allow the consumer set the topics that it's interested in!
Producer
Producer is something you use to produce/trigger an event related to specific topic inside a specific broker, once this event is triggered the interested consumers with this event topic will receive a notification about this topic
You can use this producer from anywhere inside your application, what you need is just use function called useProducer to trigger an event with the following parameters
| parameter | type | required | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| BrokerName | string | true | the name of the broker that you want to produce an event in |
| topic | string | true | A specific path that you want to trigger an event on |
| args | any | false | the rest of arguments you want to pass to the consumers that they will be called once you trigger an event related to specific topic |
import {Broker, Topic, useProducer} from "grafka";@Topic("/notification")class UserBroker extends Broker{}const makeEvent = (username:string) => {// produce an eventuseProducer("UserBroker", "/notification", username);}
As you can see the function we created will trigger an event once this function is called, this function takes one parameter which is a string that will sent it to the interested consuners once the event is triggered
Consumer
This is the interested things in your broker topics, the consumer basically is a function that will be called once an event is triggered from a producer on a specific topic
You have different ways to register consumers into brokers as the following:
- Using
Consumerdecorator to decorate a method inside a class - Using
UseConsumerto inject the consumer into a specific broker
Using Consumer Decorator
Grafka exposes to you a decorator function that you can use inside any class to inject this method as a consumer inside any broker you want, this decorator can be used if you are using typescript
Example
import {Broker, Topic, useProducer, Consumer} from "grafka";@Topic("/notification")class UserBroker extends Broker{}class UserService {@Consumer(UserBroker, ["/notification"])receiveNotification() {}}const makeEvent = (username:string) => {// produce an eventuseProducer("UserBroker", "/notification", username);}
Consumer Decorator takes the following parameters
| parameter | type | required | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Broker | string/Broker | true | This parameter specifies which broker you want to inject this consumer in, this barameter can be a string to specify the name of the broker or can be a broker class instance |
| topics | Array(string) | true | specifies the topics that this consumer is interested in |
| args | any | false | the rest of arguments that you want to pass to the consumer when it's called once the event is triggered |
Using UseConsumer Method
If you don't want to use decorators, you can use UseConsumer method which is can be used anywhere to inject a consumer into a specific broker
Example
import {Broker, Topic, useProducer, Consumer, UseConsumer} from "grafka";@Topic("/notification")class UserBroker extends Broker{}const NotificationConsumer = () => {console.log("this is consumer");}UseConsumer(UserBroker || "userBroker", ["/notification"], NotificationConsumer)const makeEvent = (username:string) => {// produce an eventuseProducer("UserBroker", "/notification", username);}
UseConsumer takes the following parameters:
| parameter | type | required | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Broker | string/Broker | true | This parameter specifies which broker you want to inject this consumer in, this barameter can be a string to specify the name of the broker or can be a broker class instance |
| topics | Array(string) | true | specifies the topics that this consumer is interested in |
| executer | function | true | a function should be executed when a producer fires an event related to one of this consumer topics |
| args | any | false | the rest of arguments that you want to pass to the consumer when it's called once the event is triggered |
When you use UseConsumer function or Consumer decorator, you can specify the topics that this consumer is interested in, if one of the specified topics is not defined in the broker before, the consumer function will add it automatically to the specified broker topics
Use The Broker
After defining the broker, now you need to use this broker to activate it and make it available to be consumed be producers and consumers, for that Grafka introduce a function called UseBroker this function can be used as a class decorator or can be used as a standalone function
UseBroker function parameters are as the following:
| parameters | type | required | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Broker | Broker | true | this is the broker that you want to add to the consumed brokers |
Exampl
import {Broker, Topic, useProducer, Consumer, UseConsumer, UseBroker} from "grafka";@Topic("/notification")class UserBroker extends Broker{}// use this brokerUseBroker(UserBroker);
If you want to use this function as a class decorator, you can write something like this:
Exampl
import {Broker, Topic, useProducer, Consumer, UseConsumer, UseBroker} from "grafka";// use this broker@UseBroker@Topic("/notification")class UserBroker extends Broker{}
Note
the UseBroker decorator should be used at the top of the class other decorators